How to Check Website Cache in 2025?
Great question — the old cache:domain.com trick still works sometimes, but it's unreliable; many sites disable or don’t expose their cache that way now. In 2025, there are better or more consistent ways to check a site’s cached version (from Google, Bing, or other sources). Here are updated methods, tools, tips, and caveats.
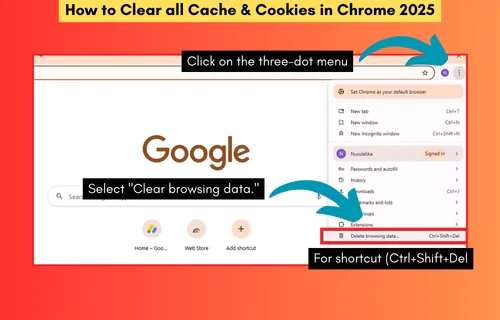
Great question — the old cache:domain.com trick still works sometimes, but it's unreliable; many sites disable or don’t expose their cache that way now. In 2025, there are better or more consistent ways to check a site’s cached version (from Google, Bing, or other sources). Here are updated methods, tools, tips, and caveats.
Methods to Check Website Cache Today
1. Google “Cached” via Search Results
-
Go to Google, search for the page or domain.
-
In the search results listing, click the three-dot menu or the down‐arrow next to the URL. If available, there will be a “Cached” link.
-
Or type in search bar:
cache:example.com/page.html— but as you said, this doesn’t always show.
2. Google Search Console “URL Inspection” Tool
-
If you own the site (or have access), use the URL Inspection tool in Search Console.
-
It will show “View Crawled Page”, and sometimes a “Cached Page” preview or snapshot.
-
This is one of the most reliable ways for your own site.
3. Bing Cache
-
Bing still supports
cache:queries more reliably in many cases. -
Or search the site in Bing, click down-arrow next to URL to see “Cached page”.
4. Web Archive / Archive.org
-
Use archive.org or Wayback Machine to see historical snapshots.
-
Good for seeing older versions or when Google’s cache is unavailable.
5. Third-Party Tools / Services
-
Websites or SEO tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, Siteliner, Wayback Browser extensions often provide cache snapshots.
-
Tools like “CachedView” (cachedview.com) aggregate multiple caches (Google, Bing, Archive) in one interface.
6. Using curl or Developer Tools (via headers)
-
Sometimes servers send
X-CacheorX-Google-Cacheheaders when serving a cached HTML version. You can inspect this in DevTools → Network tab, or via:Look for headers like:
7. Using Google’s “text-only” cache archive
-
Append
&output=html_textto a Google cached URL, e.g.:This sometimes fetches a text-only version.
Tips & Caveats
-
Many websites disable Google’s “cache” view via meta tags like
to prevent their pages from being cached publicly. -
If site uses dynamic content / JS rendering, the cached version might not display everything (some content may be missing).
-
Some SEO tools cache snapshots of pages, but those snapshots may be stale (days/weeks old).
-
Always check the timestamp of the cached version (usually Google shows “Cached — date”).
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0